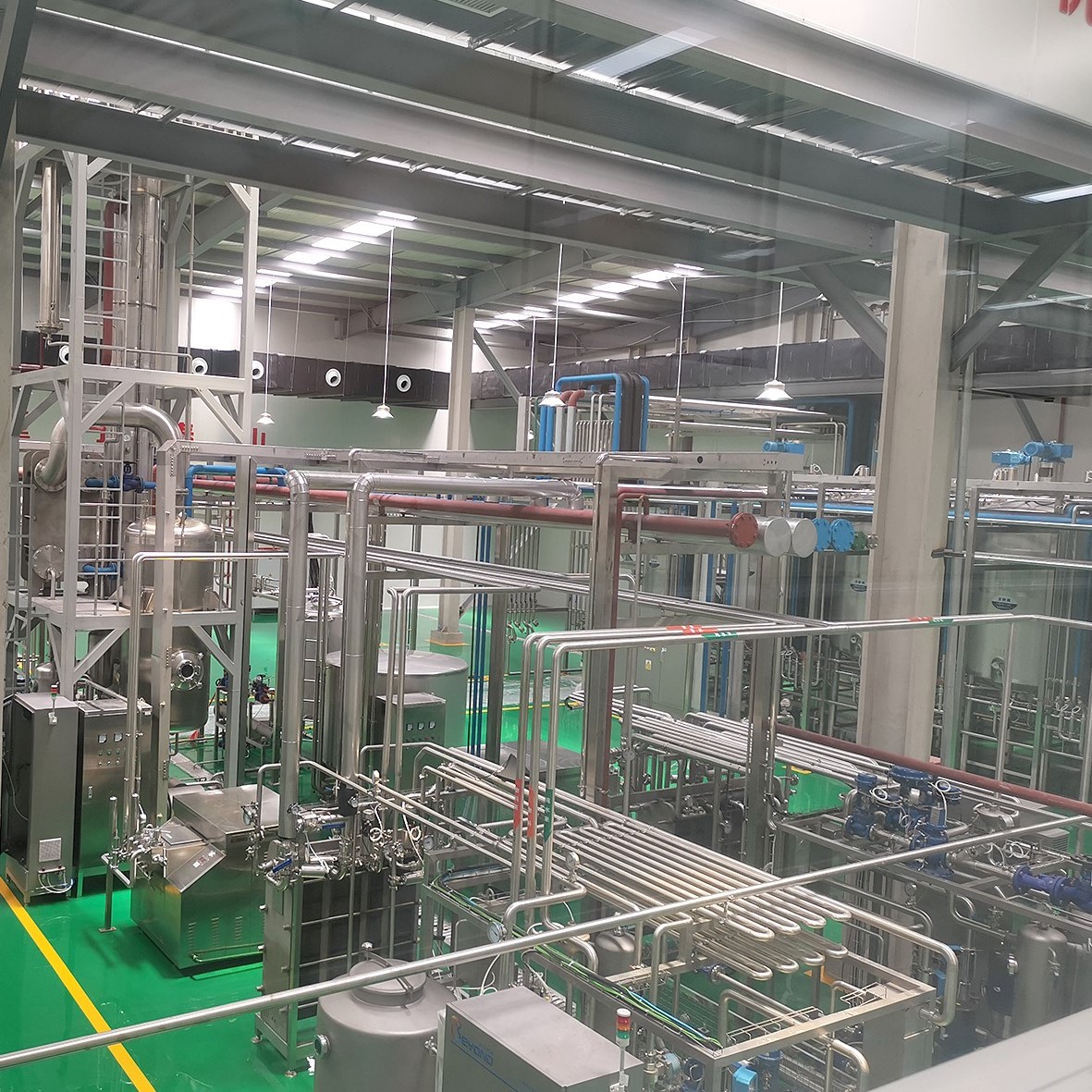
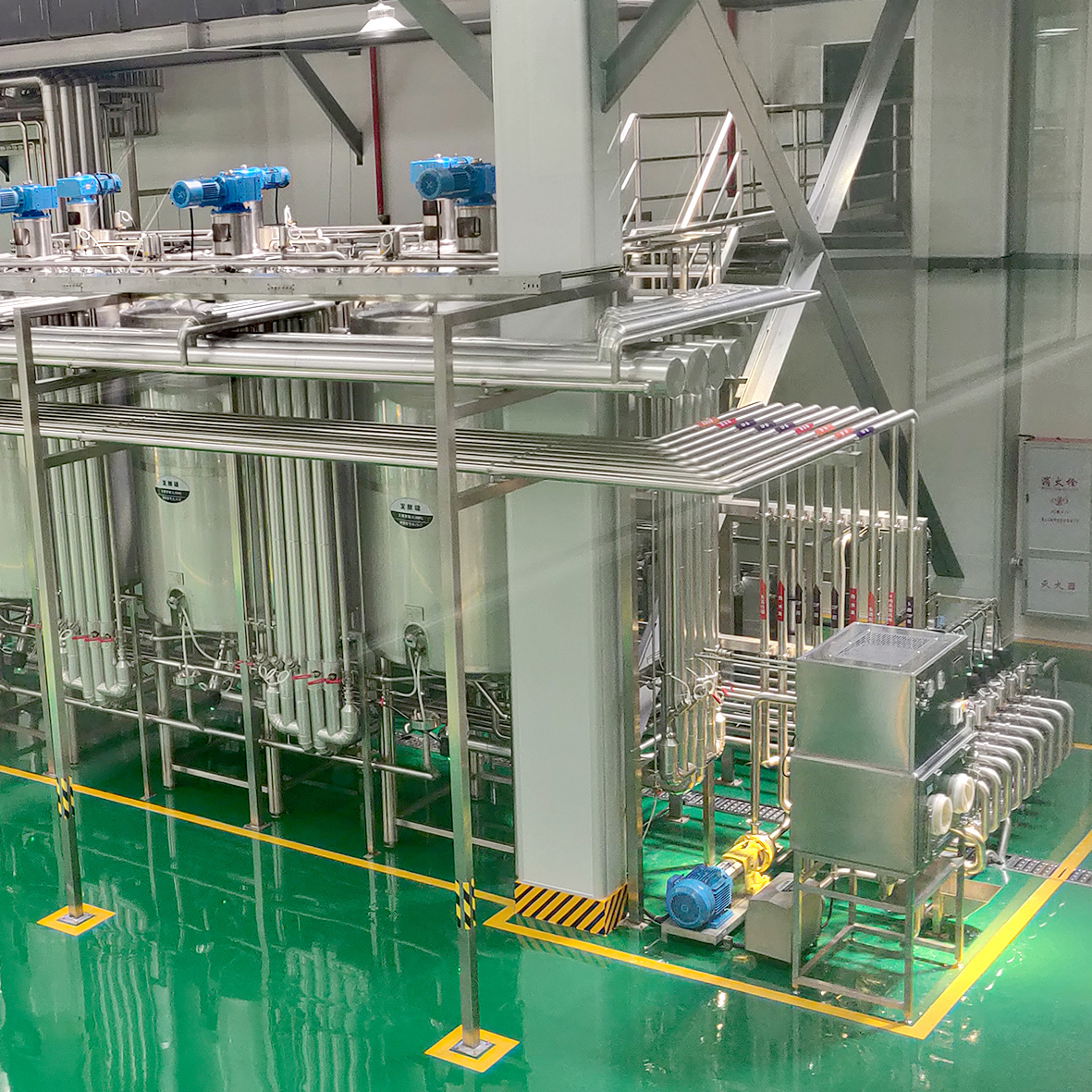
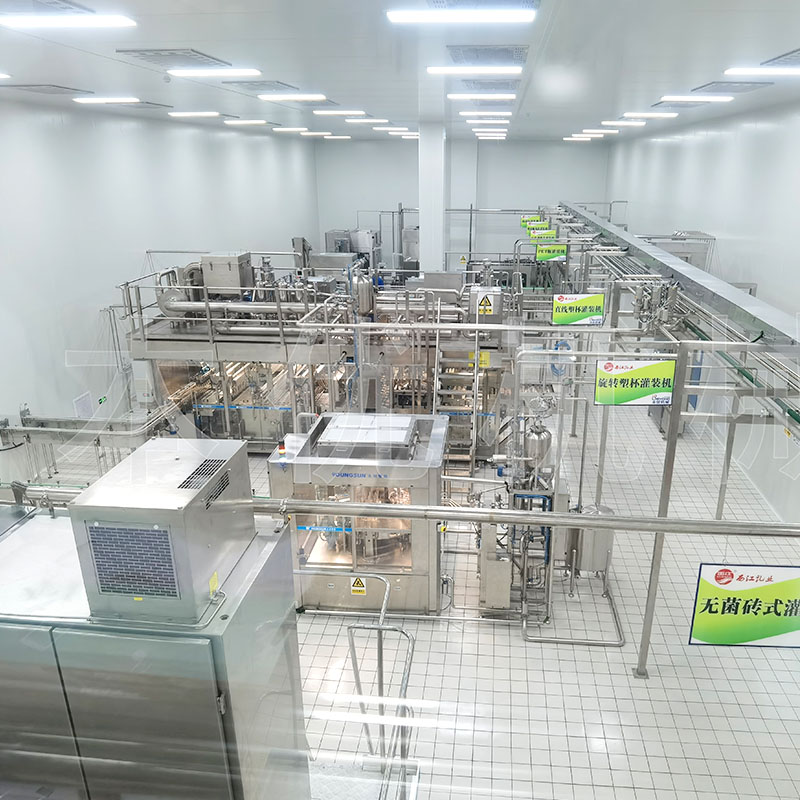
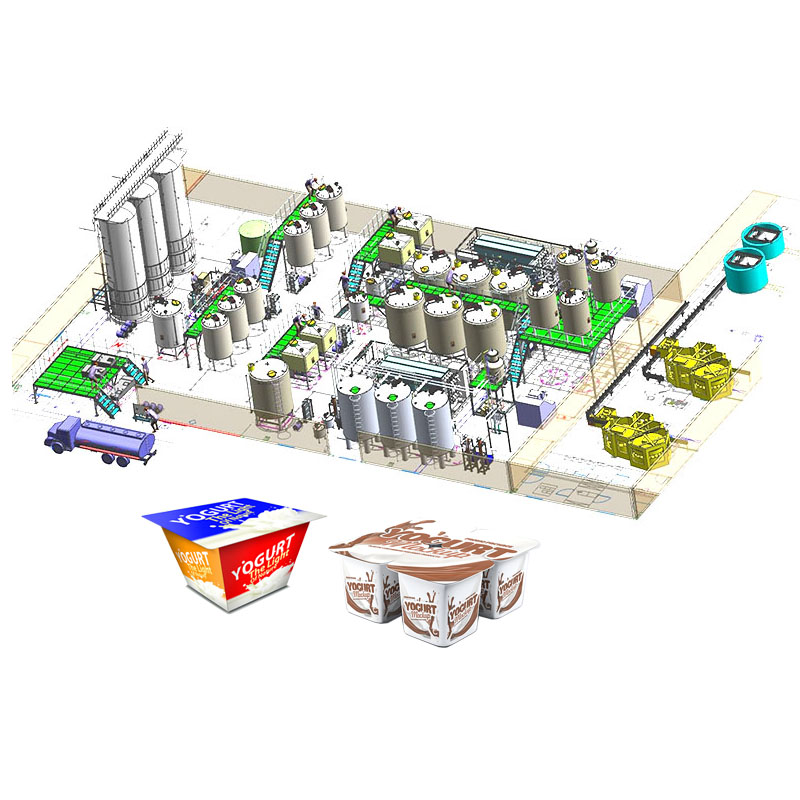
A yogurt processing line is a series of equipment and machinery used to produce yogurt in a large-scale production setting. The line typically includes various stages and processes, such as milk reception, milk storage, pasteurization, homogenization, fermentation, cooling, flavoring, filling, packaging, and labeling.
Milk Reception: Raw milk is received and tested for quality before it is stored in designated tanks.
Milk Storage: Milk is stored in temperature-controlled tanks to maintain its freshness and quality.
Pasteurization: The milk is heated to specific temperatures to kill harmful bacteria while preserving beneficial enzymes and nutrients.
Homogenization: The milk is then homogenized to ensure a consistent texture and prevent separation of cream.
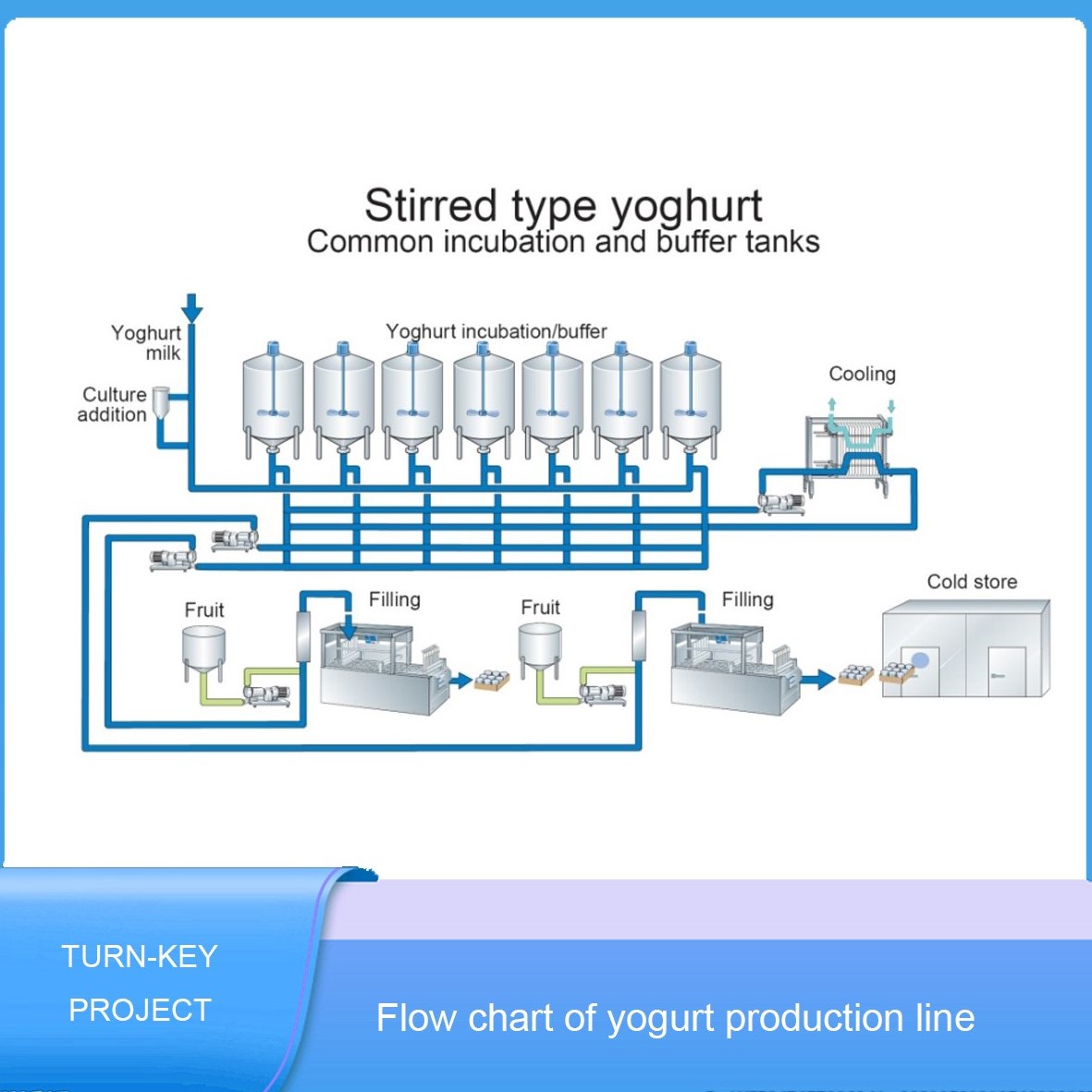
Fermentation: The milk is inoculated with live cultures of bacteria (such as Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus) and incubated at controlled temperatures to allow the fermentation process to occur.
Cooling: Once the desired fermentation time is reached, the yogurt is cooled to stop the fermentation process and stabilize the product.
Flavoring: Flavors, fruits, or other additives are added to the yogurt to enhance taste and texture.
Filling: The yogurt is filled into individual containers, such as cups or bottles, through automated filling machines.
Packaging: The filled containers are then sealed, either by heat-sealing or using lids, and prepared for further processing.
Labeling: The containers are labeled with product information, including nutritional facts, ingredients, and branding.
Quality Control: Throughout the process, quality control measures are implemented to ensure that the yogurt meets the desired standards for taste, texture, and safety.
Storage and Distribution: The packaged yogurt is stored in appropriate conditions before being distributed to retailers or consumers.
Raw materials and products of yogurt processing line
1. Raw materials
In yogurt processing line, the main raw materials are raw milk and other auxiliary raw materials. The following is a detailed list of raw materials:
•Raw milk: Fresh milk directly obtained from dairy farms or pastures is the basic raw material for producing yogurt. The quality of raw milk directly affects the quality of the final product.
•Lactic acid bacteria fermentation agent: Commonly used lactic acid bacteria fermentation agents include Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus. These strains produce lactic acid during the fermentation process, which coagulates milk and gives yogurt a unique sour taste.
•Water: used for dilution, cleaning equipment and cooling process.
•Emulsifiers: such as lecithin, used to improve the stability and taste of the product.
•Stabilizers: such as carrageenan, gelatin, pectin, used to prevent product stratification and improve the texture of the product.
•Sweeteners: such as sucrose and stevia, used to increase the sweetness of the product.
•Flavor: such as vanilla flavor and fruit flavor, used to enhance the flavor of the product.
• Fruit pieces: such as strawberry, blueberry, mango, etc., used to make fruit yogurt.
• Vitamins and minerals: such as vitamin D and calcium, used to enhance the nutritional value of the product.
• Preservatives: such as potassium sorbate, used to extend the shelf life of the product.
2. Products
The yogurt processing line can produce many different types of yogurt products. The following are some common product types:
• Ordinary yogurt: No additional ingredients are added, only raw milk and lactic acid bacteria fermentation agent, to maintain the basic flavor of yogurt.
• Flavored yogurt: such as vanilla yogurt, strawberry yogurt, blueberry yogurt, etc., by adding different flavors and fruit pieces, a variety of flavors are available.
• Low-fat yogurt: Part of the fat is removed through centrifugal separation technology, suitable for people who pursue a low-fat diet.
• Skim yogurt: Almost fat-free, suitable for people who lose weight and low-fat diet.
• Greek yogurt: Excess water and whey are removed through multiple filtrations to make the yogurt thicker and taste better.
• Probiotic yogurt: Adding specific probiotics, such as Bifidobacterium, helps improve intestinal health.
•Organic yogurt: from cows on organic farms, produced in accordance with organic farming standards, without chemical pesticides and hormones.
•Plant-based yogurt: such as soy milk yogurt, almond milk yogurt, oat milk yogurt, suitable for lactose intolerance or vegetarians.

Types of yoghurt: setting type, stirring type and adding various fruit juice jam and other accessories fruit flavor yogurt.
Packing form: HDPE plastic bottle, plastic cup, plastic bag, roof bag, glass bottle
Output: 2T / D-500T / D
Main equipment system
Item
Data
Composition of yoghurt fermentation
system.
Yoghurt fermentation system
includes: online culture addition system, ultra-clean fermentation tanks
system, aseptic air system,flexible cooling system and matched pipes,
valves,instruments and control programs, etc.
online culture addition system
The online culture addition system
adopts the ultra-clean culture online addition method, which includes culture
adding tube that
ultra-clean fermentation tanks
system
The ultra-clean fermentation tanks
system mainly refers to the fermentation tanks and auxiliary configuration to
be used in the yoghurt fermentation process
Flexible cooling system
The flexible cooling system mainly
includes a large channel low flow rate plate and a constant temperature water
system. Through this system, the fermented yoghurt can be cooled to about 20℃,and the
cooling temperature difference less than 5℃dT, which
can
Aseptic air system
Aseptic air system includes SUS304
bracket, including degreasing and dewatering filter, activated carbon filter,
coarse filter,sterilizing filter, steam filter; compressed air pressure
reducing valve, steam pressure reducing valve, pressure gauge,temperature
probes, etc., this system can be steam sterilized and CIP cleaned.It is used
for the protection of micro positive pressure in the tank during the fermentation
process, which can prevent the materials in the tank from being contaminated
can fit different types of cultures and an aseptic filter air positive
pressure protective cover that reaches a 100-level purification level
minimize the damage of the yoghurt viscosity, which can achieve better
post-fermentation effect.
by the outside enviroment.
Equipment list sample of complete yogurt processing line
|
Equipment list of complete yogurt processing line (pasteurized milk/yogurt/cheese/cream/butter) |
|
| Name | Main technology parameter |
| Milk receive, storage and cream separator unit | |
| Electron pound scale | Maximum weighing 500KG |
| Milk weighing tank | SUS304, single layer, product feeded in through 40 mesh filter net, CIP cleaning ball |
| Milk acceptor | SUS304, single layer, CIP cleaning ball |
| Milk pump | SUS304, pump lift 24m, hard alloy mechanical seal, inner shell mirror polished |
| Twin piping filter | SUS304, two pipe, stainless steal filter element 100 mesh |
| Dish separator | Auto residue discharge |
| Chiling tank | SUS304, alveolate jacket, attached with compressor |
| Milk pump | SUS304, pump lift 24m, hard alloy mechanical seal, inner shell mirror polished |
| Preparing unit | |
| Blending tank | SUS304, heat insulated, top off center vertical agitator, conical head, airtight manhole, breather valve, digital readout thermometer, anti-eddy baffle, supporters with adjustable feet |
| Milk pump | SUS304, pump lift 24m, hard alloy mechanical seal, inner shell mirror polished |
| Mini set of plate-type heat exchanger | SUS304, two stages |
| High speed emulsification tank | SUS304, heat insulated, bottom high speed emulsifier, digital readout thermometer,s upporters with adjustable feet |
| Milk pump | SUS304, pump lift 24m, hard alloy mechanical seal, inner shell mirror polished |
| Twin piping filter | SUS304, two pipe, stainless steal filter element 100 mesh |
| Sterilizing and homogenizing unit | |
| UHT sterilizer | Tub-type, sterilzing temperature 137 C, holding time 4s, full automatic control |
| High pressure homogenizer | 40MPa (starting box included) |
| Temperature holding | SUS304, holding 300s |
| Distributing plate | SUS304, 3 holes |
| Cheese/butter processing unit | |
| Bufferying tank | SUS304, heat insulated, top off center vertical agitator, conical head, airtight manhole, breather valve, digital readout thermometer, anti-eddy baffle, supporters with adjustable feet |
| Milk pump | SUS304, pump lift 24m, hard alloy mechanical seal, inner shell mirror polished |
| Cream seperator | |
| Bufferying container | SUS304, with cover |
| Milk pump | SUS304, pump lift 24m, hard alloy mechanical seal, inner shell mirror polished |
| Butter churner | SUS304, stepless timing |
| Cheese vat | SUS304, with heating jacket and insising device |
| Pressor | SUS304, 6 heads |
| Mould | SUS304, 10L, with cover |
| Yogurt fermentation unit | |
| Fermentation tank | SUS304, heat insulated, top off center vertical agitator, conical head, airtight manhole, breather valve, digital readout thermometer, anti-eddy baffle, supporters with adjustable feet |
| Rotary pump | SUS304, hard alloy mechanical seal, manual stepless shift |
| Plate cooler | SUS304, single stage, milk discharge at 4C |
| Rotary pump | SUS304, hard alloy mechanical seal, manual stepless shift |
| Filling unit | |
| Higher position tank | SUS304, heat insulated, top off center vertical agitator, conical head, airtight manhole, breather valve, digital readout thermometer, anti-eddy baffle, supporters with adjustable feet |
| Pasteurized milk filling machine | |
| Yogurt filling machine | |
| CIP system unit | |
| Semi-auto CIP system | Outer shell of SUS304, inner shell of SUS316, single cleaning way, concentrated acid/alkali tank adding system based on US technology, 100L×2 acid/alkali concentrate tanks |
| CIP return pump | SUS304, pump lift 24m, hard alloy mechanical seal, inner shell mirror polished |
| Installation part |
Whole milk processing line installation and commissioning |
Yogurt Processing Line installation and debugging
The installation and debugging of a yogurt processing line is a complex process that involves several stages to ensure the equipment functions optimally, maintains hygiene standards, and adheres to food safety regulations.
Below is a general guide on how this process typically unfolds:
1. Site Preparation• Clearance and Cleaning: The installation area must be cleared of any debris and thoroughly cleaned before the equipment arrives. This includes sanitizing the floors, walls, and ceiling.• Infrastructure Check: Verify that the site has appropriate water supply, drainage, electricity supply (including voltage compatibility), and ventilation systems in place.
2. Equipment Unloading and Placement• Unpacking: Carefully unpack each piece of equipment, inspecting for any damage during transportation.• Placement: Position the equipment according to the layout plan provided by the manufacturer or engineer. Consider workflow efficiency, ease of maintenance, and accessibility for cleaning when deciding on the placement.
3. Assembly and Installation• Assembly: Follow the manufacturer's instructions to assemble the various parts of the processing line. This may involve connecting tanks, pumps, homogenizers, pasteurizers, fillers, and packaging machines.• Piping and Wiring: Install the necessary pipelines for milk supply, water, steam, and cleaning solutions. Also, wire the electrical components, ensuring all connections are waterproof and conform to safety standards.
4. Calibration and Alignment• Equipment Calibration: Calibrate instruments such as temperature sensors, flow meters, and timers to ensure accuracy.• Alignment: Ensure all machinery is properly aligned to prevent leaks, reduce wear, and promote efficient operation.
5. Utility Connections• Water and Steam: Connect to the water supply and steam generator, making sure all connections are leak-proof.• Refrigeration System: If applicable, connect the cooling system to maintain the required temperatures for fermentation and storage.
6. Sanitization and Sterilization• Cleaning: Thoroughly clean all equipment before use, using appropriate cleaning agents.• Sterilization: Sterilize the entire system to eliminate any potential contaminants, following industry guidelines.
7. Testing and Debugging• Trial Run: Conduct a trial run of the entire processing line without actual product to check for any mechanical or operational issues.• Debugging: Identify and fix any problems encountered during the trial run. This may include adjusting settings, tightening connections, or replacing faulty parts.• Product Testing: Once the system is operating smoothly, conduct a test production run with a small batch of yogurt to assess product quality and taste.
8. Optimization and Training• Process Optimization: Fine-tune the process parameters for maximum efficiency and product quality.• Staff Training: Train the operating staff on the proper usage, cleaning, and maintenance procedures for each piece of equipment.
9. Documentation and Compliance• Documentation: Record all installation, testing, and calibration data for future reference and compliance purposes.• Compliance Check: Ensure the installation adheres to local health and safety regulations, as well as industry-specific standards .
Yogurt Processing Line Customization Solution
Customizing a yogurt processing production line requires comprehensive consideration of multiple aspects such as production scale, product types, automation level, and food safety standards. Here is a detailed overview of the customization plan:
1. Preliminary planning and design
• Demand analysis: Clarify production scale (such as daily output), product types (such as traditional yogurt, Greek yogurt, flavored yogurt, etc.), and target markets.
• Factory layout: Design the production line layout based on available space to ensure smooth and hygienic processes for raw material input, processing, filling, packaging, and finished product output.
Hygiene design: Using easy to clean materials to ensure that all equipment and pipelines meet food safety and hygiene requirements, and designing a CIP cleaning system.
2. Raw material reception and pretreatment
Raw milk receiving station: equipped with an automated milk truck unloading system for preliminary quality testing.
• Pre processing: including cooling, filtering, standardization (adjusting fat content), homogenization (refining fat particles to enhance taste), and pasteurization.
3. Fermentation system
Fermentation tank: Customized in size according to production scale, equipped with precise temperature control system to ensure constant fermentation temperature, supporting different types of fermentation program settings.
• Strain addition: A sterile addition system is used to ensure stable addition and even distribution of active strains.
4. Cooling and ripening
• Rapid cooling: After fermentation is complete, quickly cool to refrigeration temperature, stop the fermentation process, and lock in the taste and nutritional value of yogurt.
Post ripening: Let the yogurt stand at a specific temperature for a period of time to make the texture more delicate and the flavor better.
5. Filling and packaging
Filling machine: Select or customize filling equipment according to packaging specifications (cup, bottle, bag, etc.), supporting aseptic filling technology.
• Capping and labeling: Automatic completion of capping and labeling ensures packaging integrity and aesthetics.
Diversified packaging: Considering the expansion of future product lines, equipment should have a certain degree of flexibility in adjusting packaging formats.
6. Quality Control and Traceability
Online monitoring: Set up quality control points, such as pH and viscosity testing, to ensure that the product meets standards.
Traceability system: Establish batch management and product traceability systems to achieve full chain traceability from raw materials to finished products.
7. Automation and Control Systems
PLC/SCADA system: Implement automated control and monitoring of production lines, improve production efficiency, and reduce human errors.
Data collection and analysis: Collect production data for production efficiency analysis and continuous improvement.
8. Post treatment and environmental protection
• Waste disposal: Design wastewater and waste disposal systems that meet environmental requirements.
Energy efficiency: Choose energy-saving equipment, such as heat recovery systems, to reduce energy consumption.
9. Training and after-sales service
• Operation training: Provide comprehensive equipment operation and maintenance training for operators.
After sales service: Ensure that suppliers provide timely technical support and spare parts supply.
Through the detailed customization plan mentioned above, an efficient, flexible, and food safety compliant yogurt processing production line can be constructed to meet specific market demands and production goals.